TREATMENT
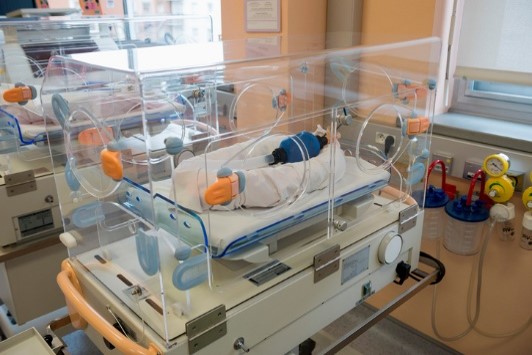
The neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) or special care nursery provides round-the-clock care for your premature baby.
Intensive care for your premature baby
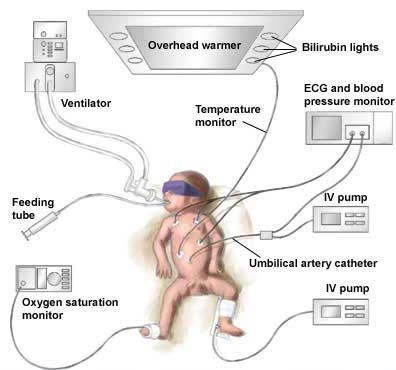
In the neonatal intensive care unit, your baby will likely receive fluids and nutrients through an intravenous (IV) catheter,
and later start breast milk or formula feedings through a tube slid through his or her nose or mouth.
Sensors may monitor your baby's blood pressure, heart rate, breathing
and temperature, and a ventilator may be used to help your baby breathe.
Specialized supportive care
Specialized supportive care for your baby may include:
- Being placed in an incubator,
Your baby will probably stay in an enclosed plastic bassinet (incubator) that's kept warm to help your baby maintain normal body temperature.
- Monitoring of your baby's vital signs. ,
Sensors may be taped to your baby's body to monitor blood pressure, heart rate, breathing and temperature. A ventilator may be used to help your baby breathe.
- Having a feeding tube.,
At first your baby may receive fluids and nutrients through an intravenous (IV) tube. Breast milk may be
given later through a tube passed through your baby's nose and into his or her stomach (nasogastric, or NG, tube).
When your baby is strong enough to suck, breast-feeding or bottle-feeding is often possible.
- Replenishing fluids,
Your baby needs a certain amount of fluids each day, depending upon his or her age and
medical conditions. The NICU team will closely monitor fluids, sodium and potassium levels to make sure that your baby's
fluid levels stay on target. If fluids are needed, they'll be delivered through an IV line
- Spending time under bilirubin lights,
The lights help your baby's system break down excess bilirubin, which builds up
because the liver can't process it all. While under the bilirubin lights, your baby
will wear a protective eye mask to rest more comfortably.
- Receiving a blood transfusion,
Your preterm baby may need a blood transfusion to raise blood volume
|
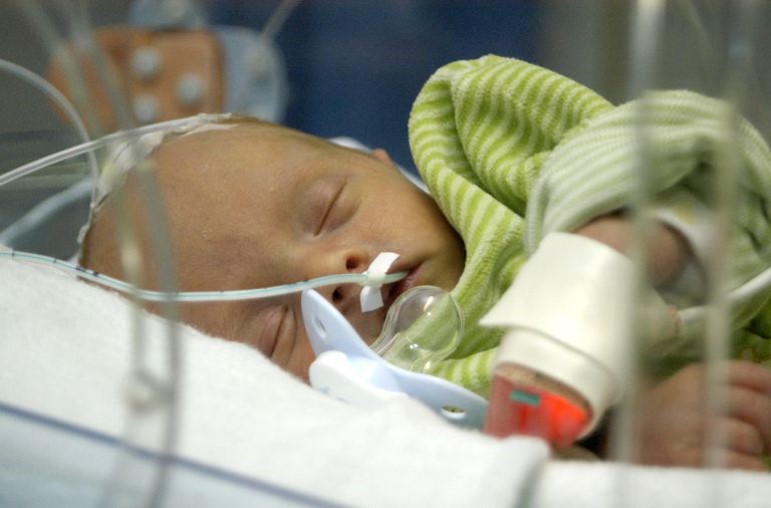
Feeding the preemie through feeding tube
|
|
Medications
Medications may be given to your baby to promote maturing and to stimulate normal functioning of the
lungs, heart and circulation.
Depending on your baby's condition, medication may include:
- Surfactant,a medication used to treat respiratory distress syndrome
- Fine-mist (aerosolized) or IV medication to strengthen breathing and heart rate
- Antibiotics if infection is present or if there's a risk of possible infection
- Medicines that increase urine output (diuretics) to manage excess fluid
- An injection of medication into the eye to stop the growth of new blood vessels that could cause retinopathy of prematurity
Surgery
Sometimes surgery is necessary to treat a number of conditions associated with prematurity. Talk with your baby's health care team to understand which
complications may require surgery, and learn about the type of surgery that might be necessary to treat them.